
Therefore, the formula to calculate the maximum speed of water is, v K / D. Since, the maximum value of K for level flow is 2000. The viscosity coefficient, 0.001 N-s/m 2. Solution: Given that, The diameter of the pipe, D 2 cm 0.02 m. We determined the water content of rhyolite glass at temperatures between 350° and 850☌ and water pressures between zero and 68.9 bars. The viscosity coefficient for water is 0.001 N-s/m 2. The viscosities range from log η = 9.5 to 14.5. A comparison of the compaction rate curves of the Pyrex with those of the rhyolite glass allowed us to determine the viscosity associated with each of our rhyolite glass compaction curves. Since we knew the viscosity of the Pyrex as a function of temperature, we could assign a viscosity to each of the Pyrex compaction rate curves. A similar set of compaction curves was constructed for Corning Pyrex 7740 glass under known temperature and compaction load (but zero water pressure). Our technique was to construct a compaction rate curve for the rhyolite glass under known conditions of temperature, water pressure, and compaction load.

VISCOSITY WATER PLUS
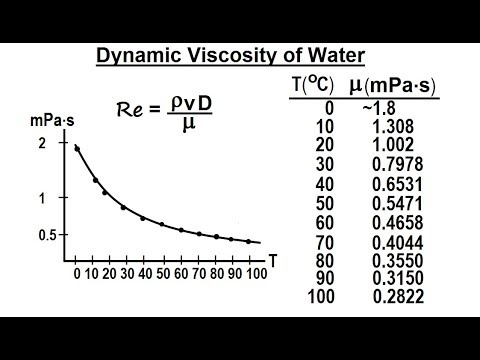
When viscous force plus buoyant force becomes equal to force due to gravity, the net force becomes zero. It gives the relationship between retarding force and velocity. Then according to Stokes law, the viscous drag force, As a result, the body experiences a retarding force. When a spherical body moves down through an infinite column of highly viscous liquid, it drags the layer of the liquid in contact with it. Existing viscosity data on water and steam are critically surveyed and correlated into an equation which represents the viscosity behavior reported by. Stoke’s law was established by an English scientist Sir George G Stokes (1819-1903). Where η is the coefficient of viscosity of the liquid. This force depends upon the area of the layer, velocity of the layer, and the distance of the layer from the surface. When liquid flows over flat surface, a backward viscous force acts tangentially to every layer. Thus, it is the resistance of a fluid to flow. Viscosity is the property of a fluid by virtue of which an internal resistance comes into play when the liquid is in motion, and opposes the relative motion between its different layers. To determine the coefficient of viscosity of a given viscous liquid by measuring terminal velocity of a given spherical body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
